一、Spring Security简介
Spring Security是为基于Spring的应用程序提供声明式安全保护的安全性框架,它提供了完整的安全性解决方案,能够在web请求级别和方法调用级别处理身份证验证和授权。因为基于Spring框架,所以Spring Security充分利用了依赖注入和面向切面的技术。
Spring Security主要是从两个方面解决安全性问题:
-
web请求级别:使用Servlet规范中的过滤器(Filter)保护Web请求并限制URL级别的访问。
-
方法调用级别:使用Spring AOP保护方法调用,确保具有适当权限的用户才能访问安全保护的方法。
想深入了解Spring Security的相关概念与实现原理,可点击传送门 ==》 Spring Security的基本原理
二、Spring Security之Web请求级别的安全性Demo
1、新建一个Spring项目,pom里添加springsecurity的依赖。
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、创建Spring Security的配置类
package com.spring.security.springsecurity.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableWebSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;
import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity //启用Web安全功能
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.authorizeRequests()
//访问"/"和"/home"路径的请求都允许
.antMatchers("/", "/home","/staff","/staff/*")
.permitAll()
//而其他的请求都需要认证
.anyRequest()
.authenticated()
.and()
//修改Spring Security默认的登陆界面
.formLogin()
.loginPage("/login")
.permitAll()
.and()
.logout()
.permitAll();
}
@Override
protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception{
//基于内存来存储用户信息
auth.inMemoryAuthentication().passwordEncoder(new BCryptPasswordEncoder())
.withUser("user").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("123")).roles("USER").and()
.withUser("admin").password(new BCryptPasswordEncoder().encode("456")).roles("USER","ADMIN");
}
}代码解析:
@EnableWebSecurity注解:启用Web安全功能(但其本身并没有什么用处,Spring Security的配置类还需实现WebSecurityConfigurer或继承WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter类,本Demo中采用后者,因为更简单去配置使用)。
@EnableWebMvcSecurity注解:在Spring 4.0中已弃用。
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter类:可以通过重载该类的三个configure()方法来制定Web安全的细节。
1、configure(WebSecurity):通过重载该方法,可配置Spring Security的Filter链。
2、configure(HttpSecurity):通过重载该方法,可配置如何通过拦截器保护请求。
保护路径的配置方法
| 方法 | 能够做什么 |
|---|---|
| access(String) | 如果给定的SpEL表达式计算结果为true,就允许访问 |
| anonymous() | 允许匿名用户访问 |
| authenticated() | 允许认证过的用户访问 |
| denyAll() | 无条件拒绝所有访问 |
| fullyAuthenticated() | 如果用户是完整认证的话(不是通过Remember-me功能认证的),就允许访问 |
| hasAnyAuthority(String…) | 如果用户具备给定权限中的某一个的话,就允许访问 |
| hasAnyRole(String…) | 如果用户具备给定角色中的某一个的话,就允许访问 |
| hasAuthority(String) | 如果用户具备给定权限的话,就允许访问 |
| hasIpAddress(String) | 如果请求来自给定IP地址的话,就允许访问 |
| hasRole(String) | 如果用户具备给定角色的话,就允许访问 |
| not() | 对其他访问方法的结果求反 |
| permitAll() | 无条件允许访问 |
| rememberMe() | 如果用户是通过Remember-me功能认证的,就允许访问 |
Spring Security 支持的所有SpEL表达式如下:
| 安全表达式 | 计算结果 |
| authentication | 用户认证对象 |
| denyAll | 结果始终为false |
| hasAnyRole(list of roles) | 如果用户被授权指定的任意权限,结果为true |
| hasRole(role) | 如果用户被授予了指定的权限,结果 为true |
| hasIpAddress(IP Adress) | 用户地址 |
| isAnonymous() | 是否为匿名用户 |
| isAuthenticated() | 不是匿名用户 |
| isFullyAuthenticated | 不是匿名也不是remember-me认证 |
| isRemberMe() | remember-me认证 |
| permitAll | 始终true |
| principal | 用户主要信息对象 |
3、configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder):通过重载该方法,可配置user-detail(用户详细信息)服务。
配置用户详细信息的方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| accountExpired(boolean) | 定义账号是否已经过期 |
| accountLocked(boolean) | 定义账号是否已经锁定 |
| and() | 用来连接配置 |
| authorities(GrantedAuthority…) | 授予某个用户一项或多项权限 |
| authorities(List) | 授予某个用户一项或多项权限 |
| authorities(String…) | 授予某个用户一项或多项权限 |
| credentialsExpired(boolean) | 定义凭证是否已经过期 |
| disabled(boolean) | 定义账号是否已被禁用 |
| password(String) | 定义用户的密码 |
| roles(String…) | 授予某个用户一项或多项角色 |
用户信息存储方式共有三种:
1、使用基于内存的用户存储:通过inMemoryAuthentication()方法,我们可以启用、配置并任意填充基于内存的用户存储。并且,我们可以调用withUser()方法为内存用户存储添加新的用户,这个方法的参数是username。withUser()方法返回的是UserDetailsManagerConfigurer.UserDetailsBuilder,这个对象提供了多个进一步配置用户的方法,包括设置用户密码的password()方法以及为给定用户授予一个或多个角色权限的roles()方法。需要注意的是,roles()方法是authorities()方法的简写形式。roles()方法所给定的值都会添加一个ROLE_前缀,并将其作为权限授予给用户。因此上诉代码用户具有的权限为:ROLE_USER,ROLE_ADMIN。而借助passwordEncoder()方法来指定一个密码转码器(encoder),我们可以对用户密码进行加密存储。
2、基于数据库表进行认证:用户数据通常会存储在关系型数据库中,并通过JDBC进行访问。为了配置Spring Security使用以JDBC为支撑的用户存储,我们可以使用jdbcAuthentication()方法,并配置他的DataSource,这样的话,就能访问关系型数据库了。
3、基于LDAP进行认证:为了让Spring Security使用基于LDAP的认证,我们可以使用ldapAuthentication()方法。
3、Controller层代码与前端代码
SecurityController代码如下:
package com.spring.security.springsecurity.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
@Controller
public class SecurityController {
@GetMapping(value = {"/home","/"})
public String home(){
return "home";
}
@GetMapping(value = "/hello")
public String hello(){
return "hello";
}
@GetMapping(value = "/login")
public String login(){
return "login";
}
}
home.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity3">
<head>
<title>Spring Security Example</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Welcome!</h1>
<p>Click <a th:href="@{/hello}">here</a> to see a greeting.</p>
</body>
</html>hello.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity3">
<head>
<title>Hello World!</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1 th:inline="text">Hello [[${#httpServletRequest.remoteUser}]]!</h1>
<form th:action="@{/logout}" method="post">
<input type="submit" value="Sign Out"/>
</form>
</body>
</html>login.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org"
xmlns:sec="http://www.thymeleaf.org/thymeleaf-extras-springsecurity3">
<head>
<title>Spring Security Example </title>
</head>
<body>
<div th:if="${param.error}">
Invalid username and password.
</div>
<div th:if="${param.logout}">
You have been logged out.
</div>
<form th:action="@{/login}" method="post">
<div><label> User Name : <input type="text" name="username"/> </label></div>
<div><label> Password: <input type="password" name="password"/> </label></div>
<div><input type="submit" value="Sign In"/></div>
</form>
</body>
</html>4、运行结果与分析
当我们直接访问 localhost:8080/hello 时,此时页面将跳转到 http://localhost:8080/login,这是因为SecurityConfig类配置了仅对 "/" 和 "/home"路径的请求无须登陆即可访问,而其他的请求需要认证。(注:这里端口我因为做了调整,改为了8081,大家照常访问8080端口即可。)
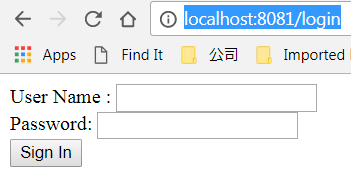
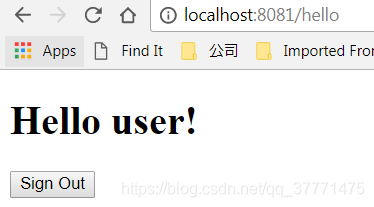
此时我们在login界面输入,我们在SecurityConfig中配置基于内存存储的用户名及密码,将成功跳转到hello界面
三、Spring Security之方法调用级别的安全性Demo
Spring Security提供了三种不同的安全注解:
- Spring Security自带的@Secured注解;
- JSR-250的@RolesAllowed注解;
- 表达式驱动的注解,包括@PreAuthorize、@PostAuthorize、@PreFilter和@PostFilter。
| 注解 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| @PreAuthorize | 在方法调用之前,基于表达式的计算结果来限制对方法的访问 |
| @PostAuthorize | 允许方法调用,但是如果表达式计算结果为false,将抛出一个安全性异常 |
| @PostFilter | 允许方法调用,但必须按照表达式来过滤方法的结果 |
| @PreFilter | 允许方法调用,但必须在进入方法之前过滤输入值 |
1、启用基于注解的方法安全性
在Spring中,如果要启用基于注解的方法安全性,关键之处在于要在配置类上使用@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity,如:
package com.spring.security.springsecurity.config;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.method.configuration.EnableGlobalMethodSecurity;
import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.method.configuration.GlobalMethodSecurityConfiguration;
@Configuration
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true,jsr250Enabled = true,prePostEnabled = true)
public class MethodSecurityConfig extends GlobalMethodSecurityConfiguration {
}
这里我们设置了securedEnabled = true,此时Spring将会创建一个切点,并将带有@Secured注解的方法防入切面中。同理,jsr250Enabled = true 与 prePostEnabled = true,分别表示启用@RolesAllowed与表达式驱动的注解。
此时配置好MethodSecurityConfig类后,我们可以在上诉代码的基础上,在SecurityController中添加一个方法:
@GetMapping(value = "/admin")
@Secured("ROLE_ADMIN")
public String admin(){
return "admin";
}admin.html界面如下:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>admin</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>admin page</h1>
</body>
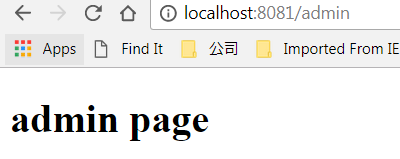
</html>此时我们如何以user用户去访问 http://localhost:8081/admin 路径,将发生403错误。

而如果以admin用户去访问 http://localhost:8081/admin 路径,将显示以下界面,表示成功访问。